Many organizations have an on-premises Active Directory infrastructure that is synced to Azure AD in the cloud. However, given that the on-prem side is the authoritative source of truth, any changes, such as disabling a user in the cloud (Azure AD), are overridden by the setting defined in the on-prem AD during the next sync. This presents challenges when you want to orchestrate a user property change from Azure that needs to persist even after the sync happens. To address the problem, this solution leverages the Automation Accounts and Hybrid Worker features across on-prem Windows resources & Azure . Automation Accounts can be used to perform cloud-based automation across Azure and non-Azure environments, including on Linux and Windows servers sitting in AWS, and GCP clouds so long as those machines have the Log Analytics agent installed.
Solution Overview
A typical use-case for this solution would flow as below:
i. Existing Azure Sentinel Analytics rule generates an incident requiring a user to be blocked from further domain access.
ii. The incident has the playbook attached to kick off the actions needed to block user access both on the cloud and on Azure AD
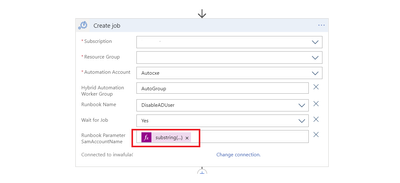
iii. The playbook includes the “create hybrid automation job” action, which executes a PowerShell script against the on-prem DC to block the user.
iv. User blocked in iii. above remains blocked even after subsequent Azure AD connect syncs with Azure cloud.
Deployment Steps
High-level summary
Before you begin to review the pre-requisites of deploying a Hybrid Runbook Worker here: Deploy a Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker in Azure Automation | Microsoft Docs
i. Create Automation Account
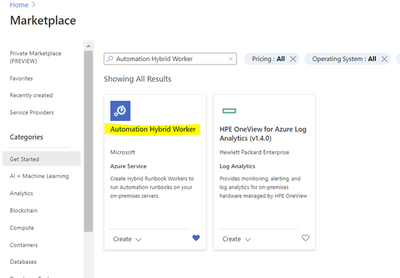
ii. Deploy the Automation Hybrid Worker solution from the Azure Market place
iii. Create a Hybrid Worker Group
iv. Create a new PowerShell Runbook.
v. Register the Hybrid Worker with Azure
vi. Test the Runbook.
vii. Deploy/build the Playbook.
viii. Attach the Playbook to the relevant Analytics rule in Azure Sentinel.
Detailed steps
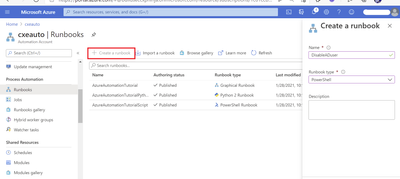
1. Create an Automation Account from the Azure Portal
2. Deploy the Automation Hybrid Worker solution from the Azure Market place
[string] $SAMAccountName
)
if (Get-Module -ListAvailable -Name ActiveDirectory) {
Write-Output “ActiveDirectory PowerShell module already exists on host.”
}
else {
Write-Output “ActiveDirectory PowerShell module does not exist on host. Installing…”
try {
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
}
catch{
Write-Error “Error installing ActiveDirectory PowerShell module.”
throw $_
break
}
Write-Output “ActiveDirectory PowerShell module installed.”
}
Write-Output “Finding and disabling user $SAMAccountName”
try {
Get-ADUser -Identity $SAMAccountName | Disable-ADAccount
}
catch {
Write-Error “Error disabling user account $SAMAccountName”
throw $_
break
}
Write-Output “Successfully disabled user account $SAMAccountName”
The script takes in a SAMAccountName parameter which it uses to find the appropriate user and disable the account. This script can be modified to do various other tasks, such as password resets, adding/removing users to/from groups, etc.
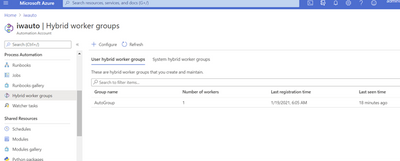
To confirm successful registration, navigate to your automation account, then select Hybrid worker groups. You should see the recently registered Hybrid Worker Group in the list in the below screenshot.
It is also recommended that you use TLS versions more recent than 1.0 and 1.1. For this reason, you may be required to run the below command as well:


Steps to orchestrate from Azure Sentinel/Logic Apps
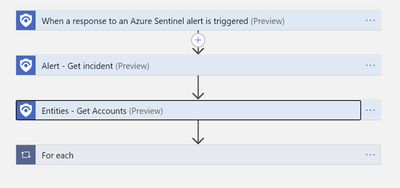
Below is the structure of the orchestration Logic App that triggers the runbook to disable qualifying accounts from the On-Prem AD. With this action, the next on-prem to cloud AD sync will maintain the state on the account – in this case disabled, until the setting is reversed from the on-prem AD Users & Computers management console.
The detailed structure of the Playbook:
Parse the JSON output from the Entities-Get Actions step above to extract the Azure User ID and SAM Account name needed to perform disable operations-first on Azure then on the On-Prem Active directory.
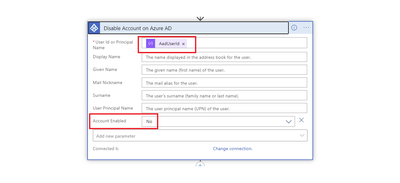
Disable Account in Azure AD

This Playbook can be deployed directly from GitHub on this link: Azure-Sentinel/Playbooks/Block-OnPremADUser at master · Azure/Azure-Sentinel (github.com)
Troubleshooting guide: Troubleshoot Azure Automation Hybrid Runbook Worker issues | Microsoft Docs
Special thanks to