This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: New blog articles in Microsoft Tech Community.
Dapr (Distributed Application Runtime) is a runtime that helps you build resilient stateless and stateful microservices. This sample shows how to deploy a Dapr application to Azure Container Apps using Terraform modules and the AzAPI Provider instead of an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) or Bicep template like in the original tutorial Deploy a Dapr application to Azure Container Apps with an Azure Resource Manager or Bicep template. You can find the code of this sample along with Terraform modules under this Azure Sample.
In this sample you will learn how to:
- Use Terraform and AzAPI Provider to deploy a microservice-based application to Azure Contains Apps.
- Create an Azure Blob Storage for use as a Dapr state store
- Deploy an Azure Container Apps environment to host one or more Azure Container Apps
- Deploy two Dapr-enabled Azure Container Apps: one that produces orders and one that consumes orders and stores them
- Verify the interaction between the two microservices.
With Azure Container Apps, you get a fully managed version of the Dapr APIs when building microservices. When you use Dapr in Azure Container Apps, you can enable sidecars to run next to your microservices that provide a rich set of capabilities. Available Dapr APIs include Service to Service calls, Pub/Sub, Event Bindings, State Stores, and Actors. In this sample, you deploy the same applications from the Dapr Hello World quickstart. The application consists of:
- A client (Python) container app to generate messages.
- A service (Node) container app to consume and persist those messages in a state store
The following architecture diagram illustrates the components that make up this tutorial:
Prerequisites
- Install Azure CLI
- An Azure account with an active subscription is required. If you don't already have one, you can create an account for free. If you don't have one, create a free Azure account before you begin.
- Visual Studio Code installed on one of the supported platforms along with the HashiCorp Terraform.
What is AzAPI Provider?
The AzAPI Provider is a very thin layer on top of the Azure ARM REST APIs. This provider compliments the AzureRM provider by enabling the management of Azure resources that are not yet or may never be supported in the AzureRM provider such as private/public preview services and features. The AzAPI provider enables you to manage any Azure resource type using any API version. This provider complements the AzureRM provider by enabling the management of new Azure resources and properties (including private preview). For more information, see Overview of the Terraform AzAPI provider.
Terraform modules
This sample contains Terraform modules to create the following resources:
- Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces: an Azure Log Analytics workspace used to collect logs and metrics of the Azure Container Apps environment.
- Microsoft.Insights/components: an Azure Application Insights used by the Azure Container Apps for logging and distributed tracing.
- Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts: this storage account is used to store state of the Dapr component.
- Microsoft.App/managedEnvironments: an Azure Container Apps environment that will host two Azure Container Apps.
- Microsoft.App/managedEnvironments/daprComponents: a state management Dapr component that hosts the orders created by the service application.
- Microsoft.App/containerApps: two dapr-enabled Container Apps: hello-k8s-node and hello-k8s-python
The following table contains the code of the modules/contains_apps/main.tf Terraform module used to create the Azure Container Apps environment, Dapr components, and Container Apps.
As you can see, the module uses an azapi_resource to create the resources. You can use an azapi_resource to fully manage any Azure (control plane) resource (API) with full CRUD. Example Use Cases:
- New preview service
- New feature added to existing service
- Existing feature / service not currently covered
For more information, see Overview of the Terraform AzAPI provider.
Deploy the sample
You can use the deploy.sh bash script to deploy the sample:
This command deploys the Terraform modules that create the following resources:
- The Container Apps environment and associated Log Analytics workspace for hosting the hello world Dapr solution.
- An Application Insights instance for Dapr distributed tracing.
- The
nodeappapp server running ontargetPort: 3000with dapr enabled and configured using:"appId": "nodeapp"and"appPort": 3000. - The
daprComponentsobject of"type": "state.azure.blobstorage"scoped for use by thenodeappfor storing state. - The headless
pythonappwith no ingress and Dapr enabled that calls thenodeappservice via dapr service-to-service communication.
Verify the result
Confirm successful state persistence
You can confirm that the services are working correctly by viewing data in your Azure Storage account.
- Open the Azure portal in your browser.
- Navigate to your storage account.
- Select Containers from the menu on the left side.
- Select state.
- Verify that you can see the file named
orderin the container. - Select on the file.
- Select the Edit tab.
- Select the Refresh button to observe updates.
View Logs
Data logged via a container app are stored in the ContainerAppConsoleLogs_CL custom table in the Log Analytics workspace. You can view logs through the Azure portal or from the command line. Wait a few minutes for the analytics to arrive for the first time before you query the logged data.
- Open the Azure portal in your browser.
- Navigate to your log analytics workspace.
- Select Logs from the menu on the left side.
- Run the following Kusto query.
ContainerAppConsoleLogs_CL
| project TimeGenerated, ContainerAppName_s, Log_s
| order by TimeGenerated desc
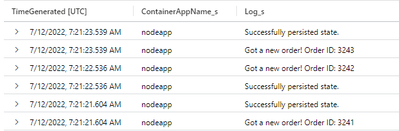
The following images shows the type of response to expect from the command.
Clean up resources
Once you are done, run the following command to delete your resource group along with all the resources you created in this tutorial.
az group delete \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
Since pythonapp continuously makes calls to nodeapp with messages that get persisted into your configured state store, it is important to complete these cleanup steps to avoid ongoing billable operations.
Next steps
- Azure Container Apps overview
- Tutorial: Deploy a Dapr application to Azure Container Apps with an Azure Resource Manager or Bicep template
- AzAPI provider
- Announcing Azure Terrafy and AzAPI Terraform Provider Previews
Conclusion
If you have any feedback, please write a comment below or submit an issue or a PR on GitHub. If you found this article and companion sample useful, please like the article below and give a star to the project on GitHub, thanks!