This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: New blog articles in Microsoft Community Hub.
This sample shows how to deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service(AKS) cluster and Azure OpenAI Service using Terraform modules with the Azure Provider Terraform Provider and how to deploy a Python chatbot that authenticates against Azure OpenAI using Azure AD workload identity and calls the Chat Completion API of a ChatGPT model.
You can find the code of the chatbot and Bicep modules to deploy the environment in this GitHub repository. For a Bicep version of the article and companion sample, see How to deploy and run an Azure OpenAI ChatGPT application on AKS via Bicep.
A chatbot is an application that simulates human-like conversations with users via chat. Its key task is to answer user questions with instant messages. Azure Kubernetes Service(AKS) cluster communicates with Azure OpenAI Service via an Azure Private Endpoint. The chatbot application simulates the original Magic 8 Ball plastic sphere, made to look like an oversized eight ball used for fortune-telling or seeking advice.
AI applications can be used to perform tasks such as summarizing articles, writing stories, and engaging in long conversations with chatbots. This is made possible by large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI ChatGPT, which are deep learning algorithms capable of recognizing, summarizing, translating, predicting, and generating text and other content. LLMs leverage the knowledge acquired from extensive datasets, enabling them to perform tasks beyond teaching AI human languages. These models have succeeded in diverse domains, including understanding proteins, writing software code, and more. Apart from their applications in natural language processing, such as translation, chatbots, and AI assistants, large language models are also extensively employed in healthcare, software development, and various other fields.
For more information on Azure OpenAI Service and Large Language Models (LLMs), see the following articles:
- What is Azure OpenAI Service?
- Azure OpenAI Service models
- Large Language Model
- Azure OpenAI Terraform deployment for sample chatbot
- Terraform module for deploying Azure OpenAI Service.
Prerequisites
- An active Azure subscription. If you don't have one, create a free Azure account before you begin.
- Visual Studio Code installed on one of the supported platforms along with the HashiCorp Terraform.
- Azure CLI version 2.49.0 or later installed. To install or upgrade, see Install Azure CLI.
aks-previewAzure CLI extension of version 0.5.140 or later installed
You can run az --version to verify above versions.
To install the aks-preview extension, run the following command:
Run the following command to update to the latest version of the extension released:
Architecture
This sample provides a set of Terraform modules to deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service(AKS) cluster and Azure OpenAI Service and how to deploy a Python chatbot that authenticates against Azure OpenAI using Azure AD workload identity and calls the Chat Completion API of the ChatGPT model. Azure Kubernetes Service(AKS) cluster communicates with Azure OpenAI Service via an Azure Private Endpoint. The following diagram shows the architecture and network topology deployed by the sample:
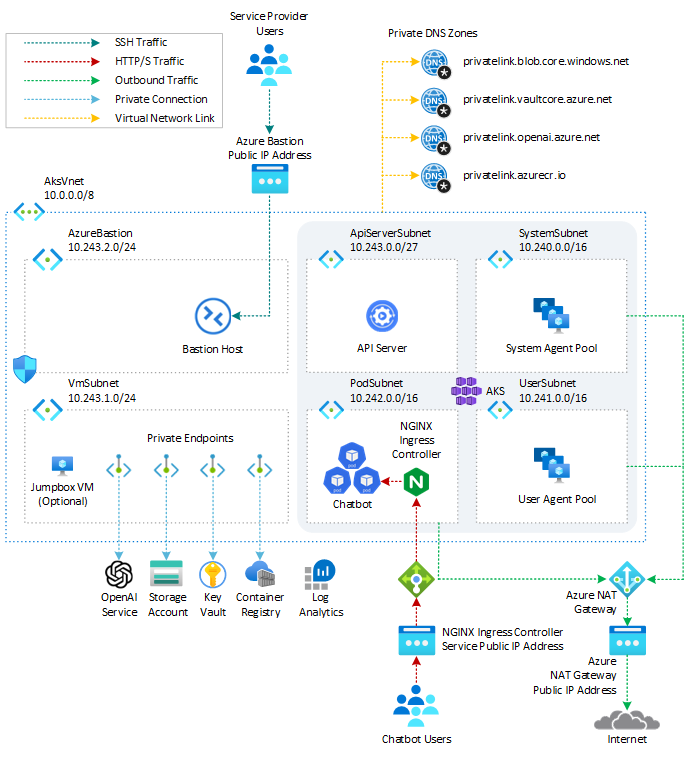
Terraform modules are parametric, so you can choose any network plugin:
- Azure CNI with static IP allocation
- Azure CNI with dynamic IP allocation
- Azure CNI Powered by Cilium
- Azure CNI Overlay
- BYO CNI
- Kubenet
In a production environment, we strongly recommend deploying a private AKS cluster with Uptime SLA. For more information, see private AKS cluster with a Public DNS address. Alternatively, you can deploy a public AKS cluster and secure access to the API server using authorized IP address ranges.
The Terraform modules deploy the following Azure resources:
- Azure OpenAI Service: an Azure OpenAI Service with a GPT-3.5 model used by the chatbot application. Azure OpenAI Service gives customers advanced language AI with OpenAI GPT-4, GPT-3, Codex, and DALL-E models with the security and enterprise promise of Azure. Azure OpenAI co-develops the APIs with OpenAI, ensuring compatibility and a smooth transition from one to the other.
- User-defined Managed Identity: a user-defined managed identity used by the AKS cluster to create additional resources like load balancers and managed disks in Azure.
- User-defined Managed Identity: a user-defined managed identity used by the chatbot application to acquire a security token via Azure AD workload identity to call the Chat Completion API of the ChatGPT model provided by the Azure OpenAI Service.
- Azure Virtual Machine: Terraform modules can optionally create a jump-box virtual machine to manage the private AKS cluster.
- Azure Bastion Host: a separate Azure Bastion is deployed in the AKS cluster virtual network to provide SSH connectivity to both agent nodes and virtual machines.
- Azure NAT Gateway: a bring-your-own (BYO) Azure NAT Gateway to manage outbound connections initiated by AKS-hosted workloads. The NAT Gateway is associated to the
SystemSubnet,UserSubnet, andPodSubnetsubnets. The outboundType property of the cluster is set touserAssignedNatGatewayto specify that a BYO NAT Gateway is used for outbound connections. NOTE: you can update theoutboundTypeafter cluster creation and this will deploy or remove resources as required to put the cluster into the new egress configuration. For more information, see Updating outboundType after cluster creation. - Azure Storage Account: this storage account is used to store the boot diagnostics logs of both the service provider and service consumer virtual machines. Boot Diagnostics is a debugging feature that allows you to view console output and screenshots to diagnose virtual machine status.
- Azure Container Registry: an Azure Container Registry (ACR) to build, store, and manage container images and artifacts in a private registry for all container deployments.
- Azure Key Vault: an Azure Key Vault used to store secrets, certificates, and keys that can be mounted as files by pods using Azure Key Vault Provider for Secrets Store CSI Driver. For more information, see Use the Azure Key Vault Provider for Secrets Store CSI Driver in an AKS cluster and Provide an identity to access the Azure Key Vault Provider for Secrets Store CSI Driver.
- Azure Private Endpoints: an Azure Private Endpoint is created for each of the following resources:
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Storage Account
- API Server when deploying a private AKS cluster.
- Azure Private DNDS Zones: an Azure Private DNS Zone is created for each of the following resources:
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Storage Account
- API Server when deploying a private AKS cluster.
- Azure Network Security Group: subnets hosting virtual machines and Azure Bastion Hosts are protected by Azure Network Security Groups that are used to filter inbound and outbound traffic.
- Azure Log Analytics Workspace: a centralized Azure Log Analytics workspace is used to collect the diagnostics logs and metrics from all the Azure resources:
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Azure Kubernetes Service cluster
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Network Security Group
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Storage Account
- Azure jump-box virtual machine
- Azure Deployment Script: a deployment script is used to run the
install-nginx-via-helm-and-create-sa.shBash script which creates the namespace and service account for the sample application and installs the following packages to the AKS cluster via Helm. For more information on deployment scripts, see Use deployment scripts
NOTE
You can find thearchitecture.vsdxfile used for the diagram under thevisiofolder.
Azure Provider
The Azure Provider can be used to configure infrastructure in Microsoft Azure using the Azure Resource Manager API's. For more information on the data sources and resources supported by the Azure Provider, see the documentation. To learn the basics of Terraform using this provider, follow the hands-on get started tutorials. If you are interested in the Azure Provider's latest features, see the changelog for version information and release notes.
What is Azure OpenAI Service?
The Azure OpenAI Service is a platform offered by Microsoft Azure that provides cognitive services powered by OpenAI models. One of the models available through this service is the ChatGPT model, which is designed for interactive conversational tasks. It allows developers to integrate natural language understanding and generation capabilities into their applications.
Azure OpenAI Service provides REST API access to OpenAI's powerful language models, including the GPT-3, Codex, and Embeddings model series. In addition, the new GPT-4 and ChatGPT model series have now reached general availability. These models can be easily adapted to your specific task, including but not limited to content generation, summarization, semantic search, and natural language-to-code translation. Users can access the service through REST APIs, Python SDK, or our web-based interface in the Azure OpenAI Studio.
The Chat Completion API, part of the Azure OpenAI Service, provides a dedicated interface for interacting with the ChatGPT and GPT-4 models. This API is currently in preview and is the preferred method for accessing these models. The GPT-4 models can only be accessed through this API.
GPT-3, GPT-3.5, and GPT-4 models from OpenAI are prompt-based. With prompt-based models, the user interacts with the model by entering a text prompt, to which the model responds with a text completion. This completion is the model’s continuation of the input text. While these models are extremely powerful, their behavior is also very sensitive to the prompt. This makes prompt construction a critical skill to develop. For more information, see Introduction to prompt engineering.
Prompt construction can be complex. In practice, the prompt acts to configure the model weights to complete the desired task, but it's more of an art than a science, often requiring experience and intuition to craft a successful prompt. The goal of this article is to help get you started with this learning process. It attempts to capture general concepts and patterns that apply to all GPT models. However, it's essential to understand that each model behaves differently, so the learnings may not apply equally to all models.
Prompt engineering refers to creating instructions called prompts for Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT. With the immense potential of LLMs to solve a wide range of tasks, leveraging prompt engineering can empower us to save significant time and facilitate the development of impressive applications. It holds the key to unleashing the full capabilities of these huge models, transforming how we interact and benefit from them. For more information, see Prompt engineering techniques.
Deploy Terraform modules
Before deploying the Terraform modules in the terraform folder, specify a value for the following variables in the terraform.tfvars variable definitions file.
Description
prefix: specifies a prefix for all the Azure resources.domain: specifies the domain part (e.g., subdomain.domain) of the hostname of the ingress object used to expose the chatbot via the NGINX Ingress Controller.subdomain: specifies the subdomain part of the hostname of the ingress object used to expose the chatbot via the NGINX Ingress Controller.namespace: specifies the namespace of the workload application that accesses the Azure OpenAI Service.service_account_name: specifies the name of the service account of the workload application that accesses the Azure OpenAI Service.ssh_public_key: specifies the SSH public key used for the AKS nodes and jumpbox virtual machine.vm_enabled: a boleean value that specifies whether deploying or not a jumpbox virtual machine in the same virtual network of the AKS cluster.location: specifies the region (e.g., westeurope) where deploying the Azure resources.admin_group_object_ids: when deploying an AKS cluster with Azure AD and Azure RBAC integration, this array parameter contains the list of Azure AD group object IDs that will have the admin role of the cluster.
We suggest reading sensitive configuration data such as passwords or SSH keys from a pre-existing Azure Key Vault resource. For more information, see Referencing Azure Key Vault secrets in Terraform.
OpenAI Terraform Module
The following table contains the code from the openai.tf Terraform module used to deploy the Azure OpenAI Service.
Azure Cognitive Services use custom subdomain names for each resource created through the Azure portal, Azure Cloud Shell, Azure CLI, Bicep, Azure Resource Manager (ARM), or Terraform. Unlike regional endpoints, which were common for all customers in a specific Azure region, custom subdomain names are unique to the resource. Custom subdomain names are required to enable features like Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for authentication. In our case, we need to specify a custom subdomain for our Azure OpenAI Service as our chatbot application will use an Azure AD security token to access it. By default, the main.tf module sets the value of the custom_subdomain_name parameter to the lowercase name of the Azure OpenAI resource. For more information on custom subdomains, see Custom subdomain names for Cognitive Services.
This terraform module allows you to pass an array containing the definition of one or more model deployments in the deployments parameter. For more information on model deployments, see Create a resource and deploy a model using Azure OpenAI.
Alternatively, you can use the Terraform module for deploying Azure OpenAI Service. to deploy an Azure OpenAI Service resource.
Private Endpoints
The main.tf module creates Azure Private Endpoints and Azure Private DNDS Zones for each of the following resources:
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Storage Account
In particular, it creates an Azure Private Endpoint and Azure Private DNDS Zone to the Azure OpenAI Service as shown in the following code snippet:
Below you can read the code of the private_dns_zone and private_endpoint modules used, respectively, to create the Azure Private Endpoints and Azure Private DNDS Zones.
private_dns_zone
private_endpoint
AKS Workload User-Defined Managed Identity
The following code snippet from the main.tf Terraform module creates the user-defined managed identity used by the chatbot to acquire a security token from Azure Active Directory via Azure AD workload identity.
The above code snippets performs the following steps:
- Creates a new user-defined managed identity.
- Assign the new managed identity to the Cognitive Services User role with the resource group as a scope.
- Federate the managed identity with the service account used by the chatbot. The following information are necessary to create the federated identity credentials:
- The Kubernetes service account name.
- The Kubernetes namespace that will host the chatbot application.
- The URL of the OpenID Connect (OIDC) token issuer endpoint for Azure AD workload identity
For more information, see the following resources:
- How to configure Azure OpenAI Service with managed identities
- Use Azure AD workload identity with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Validate the deployment
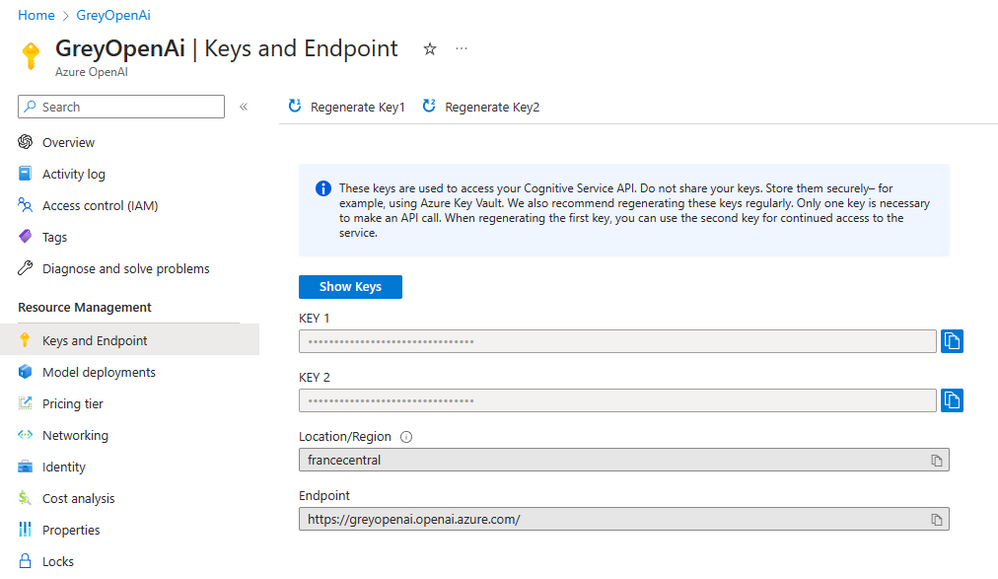
Open the Azure Portal, and navigate to the resource group. Open the Azure Open AI Service resource, navigate to Keys and Endpoint, and check that the endpoint contains a custom subdomain rather than the regional Cognitive Services endpoint.
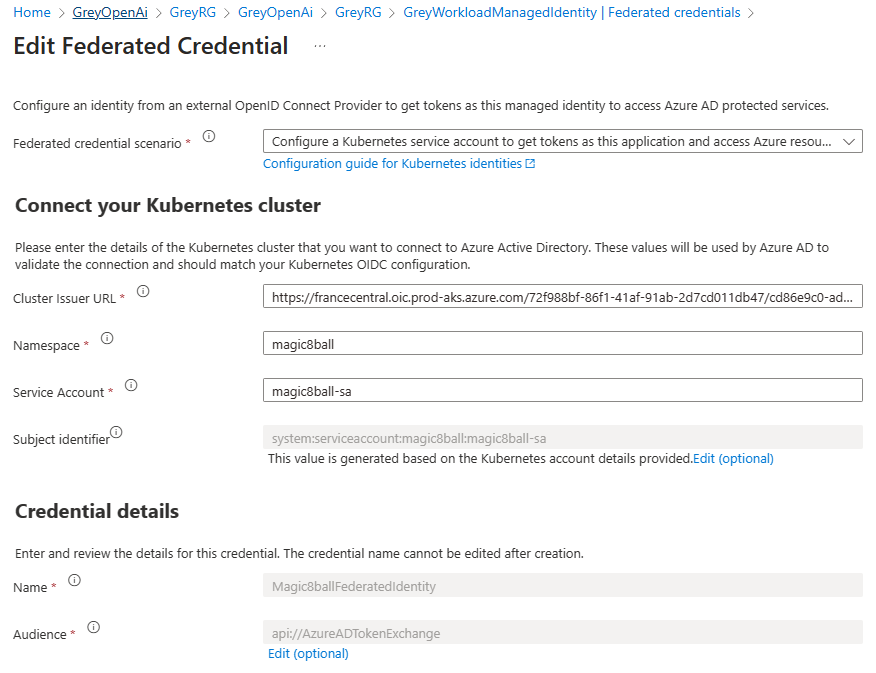
Open to the <Prefix>WorkloadManagedIdentity managed identity, navigate to the Federated credentials, and verify that the federated identity credentials for the magic8ball-sa service account were created correctly, as shown in the following picture.
Use Azure AD workload identity with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Workloads deployed on an Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS) cluster require Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) application credentials or managed identities to access Azure AD-protected resources, such as Azure Key Vault and Microsoft Graph. Azure AD workload identity integrates with the capabilities native to Kubernetes to federate with external identity providers.
Azure AD workload identity uses Service Account Token Volume Projection to enable pods to use a Kubernetes service account. When enabled, the AKS OIDC Issuer issues a service account security token to a workload, and OIDC federation enables the application to access Azure resources securely with Azure AD based on annotated service accounts.
Azure AD workload identity works well with the Azure Identity client libraries and the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) collection if you use a registered application instead of a managed identity. Your workload can use any of these libraries to authenticate and access Azure cloud resources seamlessly. For more information, see the following resources:
- Azure Workload Identity open-source project
- Use an Azure AD workload identity on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS
- Deploy and configure workload identity on an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster
- Modernize application authentication with workload identity sidecar
- Tutorial: Use a workload identity with an application on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Workload identity federation
- Use Azure AD Workload Identity for Kubernetes with a User-Assigned Managed Identity
- Use Azure AD workload identity for Kubernetes with an Azure AD registered application
- Azure Managed Identities with Workload Identity Federation
- Azure AD workload identity federation with Kubernetes
- Azure Active Directory Workload Identity Federation with external OIDC Identy Providers
- Minimal Azure AD Workload identity federation
Azure Identity client libraries
In the Azure Identity client libraries, you can choose one of the following approaches:
- Use
DefaultAzureCredential, which will attempt to use theWorkloadIdentityCredential. - Create a
ChainedTokenCredentialinstance that includesWorkloadIdentityCredential. - Use
WorkloadIdentityCredentialdirectly.
The following table provides the minimum package version required for each language's client library.
| Language | Library | Minimum Version | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| .NET | Azure.Identity | 1.9.0 | Link |
| Go | azidentity | 1.3.0 | Link |
| Java | azure-identity | 1.9.0 | Link |
| JavaScript | @azure/identity | 3.2.0 | Link |
| Python | azure-identity | 1.13.0 | Link |
Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL)
The following client libraries are the minimum version required
| Language | Library | Image | Example | Has Windows |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| .NET | microsoft-authentication-library-for-dotnet | ghcr.io/azure/azure-workload-identity/msal-net | Link | Yes |
| Go | microsoft-authentication-library-for-go | ghcr.io/azure/azure-workload-identity/msal-go | Link | Yes |
| Java | microsoft-authentication-library-for-java | ghcr.io/azure/azure-workload-identity/msal-java | Link | No |
| JavaScript | microsoft-authentication-library-for-js | ghcr.io/azure/azure-workload-identity/msal-node | Link | No |
| Python | microsoft-authentication-library-for-python | ghcr.io/azure/azure-workload-identity/msal-python | Link | No |
Deployment Script
The sample makes use of a Deployment Script to run the install-nginx-via-helm-and-create-sa.sh Bash script that creates the namespace and service account for the sample application and installs the following packages to the AKS cluster via Helm.
This sample uses the NGINX Ingress Controller to expose the chatbot to the public internet.
The install-nginx-via-helm-and-create-sa.sh Bash script can run on a public AKS cluster or on a private AKS cluster using the az aks command invoke. For more information, see Use command invoke to access a private Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster.
The install-nginx-via-helm-and-create-sa.sh Bash script returns the following outputs to the deployment script:
- Namespace hosting the chatbot sample. You can change the default
magic8ballnamespace by assigning a different value to thenamespacevariable in theterraform.tfvarsfile. - Service account name
- Prometheus namespace
- Cert-manager namespace
- NGINX ingress controller namespace
Chatbot Application
The chatbot is a Python application inspired by the sample code in the It’s Time To Create A Private ChatGPT For Yourself Today arctiel. The application is contained in a single file called app.py. The application makes use of the following libraries:
- OpenAPI: The OpenAI Python library provides convenient access to the OpenAI API from applications written in the Python language. It includes a pre-defined set of classes for API resources that initialize themselves dynamically from API responses which makes it compatible with a wide range of versions of the OpenAI API. You can find usage examples for the OpenAI Python library in our API reference and the OpenAI Cookbook.
- Azure Identity: The Azure Identity library provides Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) token authentication support across the Azure SDK. It provides a set of TokenCredential implementations, which can be used to construct Azure SDK clients that support Azure AD token authentication.
- Streamlit: Streamlit is an open-source Python library that makes it easy to create and share beautiful, custom web apps for machine learning and data science. In just a few minutes you can build and deploy powerful data apps. For more information, see Streamlit documentation
- Streamlit-chat: a Streamlit component that provides a configurable user interface for chatbot applications.
- Dotenv: Python-dotenv reads key-value pairs from a .env file and can set them as environment variables. It helps in the development of applications following the 12-factor principles.
The requirements.txt file under the scripts folder contains the list of packages used by the app.py application that you can restore using the following command:
The following table contains the code of the app.py chatbot:
The application makes use of an internal cascading style sheet (CSS) inside an st.markdown element to add a unique style to the Streamlit chatbot for mobile and desktop devices. For more information on how to tweak the user interface of a Streamlit application, see 3 Tips to Customize your Streamlit App.
Working with the ChatGPT and GPT-4 models
The generate_response function creates and sends the prompt to the Chat Completion API of the ChatGPT model.
OpenAI trained the ChatGPT and GPT-4 models to accept input formatted as a conversation. The messages parameter takes an array of dictionaries with a conversation organized by role or message: system, user, and assistant. The format of a basic Chat Completion is as follows:
The system role also known as the system message is included at the beginning of the array. This message provides the initial instructions to the model. You can provide various information in the system role including:
- A brief description of the assistant
- Personality traits of the assistant
- Instructions or rules you would like the assistant to follow
- Data or information needed for the model, such as relevant questions from an FAQ
- You can customize the system role for your use case or just include basic instructions.
The system role or message is optional, but it's recommended to at least include a basic one to get the best results. The user role or message represents an input or inquiry from the user, while the assistant message corresponds to the response generated by the GPT API. This dialog exchange aims to simulate a human-like conversation, where the user message initiates the interaction and the assistant message provides a relevant and informative answer. This context helps the chat model generate a more appropriate response later on. The last user message refers to the prompt currently requested. For more information, see Learn how to work with the ChatGPT and GPT-4 models.
Application Configuration
Make sure to provide a value for the following environment variables when testing the app.py Python app locally, for example in Visual Studio Code. You can eventually define environment variables in a .env file in the same folder as the app.py file.
AZURE_OPENAI_TYPE: specifyazureif you want to let the application use the API key to authenticate against OpenAI. In this case, make sure to provide the Key in theAZURE_OPENAI_KEYenvironment variable. If you want to authenticate using an Azure AD security token, you need to specifyazure_adas a value. In this case, don't need to provide any value in theAZURE_OPENAI_KEYenvironment variable.AZURE_OPENAI_BASE: the URL of your Azure OpenAI resource. If you use the API key to authenticate against OpenAI, you can specify the regional endpoint of your Azure OpenAI Service (e.g., https://eastus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/). If you instead plan to use Azure AD security tokens for authentication, you need to deploy your Azure OpenAI Service with a subdomain and specify the resource-specific endpoint url (e.g., https://myopenai.openai.azure.com/).AZURE_OPENAI_KEY: the key of your Azure OpenAI resource.AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT: the name of the ChatGPT deployment used by your Azure OpenAI resource, for examplegpt-35-turbo.AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL: the name of the ChatGPT model used by your Azure OpenAI resource, for examplegpt-35-turbo.TITLE: the title of the Streamlit app.TEMPERATURE: the temperature used by the OpenAI API to generate the response.SYSTEM: give the model instructions about how it should behave and any context it should reference when generating a response. Used to describe the assistant's personality.
When deploying the application to Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) these values are provided in a Kubernetes ConfigMap. For more information, see the next section.
OpenAI Library
In order to use the openai library with Microsoft Azure endpoints, you need to set the api_type, api_base and api_version in addition to the api_key. The api_type must be set to 'azure' and the others correspond to the properties of your endpoint. In addition, the deployment name must be passed as the engine parameter. In order to use OpenAI Key to authenticate to your Azure endpoint, you need to set the api_type to azure and pass the OpenAI Key to api_key.
For a detailed example of how to use fine-tuning and other operations using Azure endpoints, please check out the following Jupyter notebooks:
To use Microsoft Active Directory to authenticate to your Azure endpoint, you need to set the api_type to azure_ad and pass the acquired credential token to api_key. The rest of the parameters need to be set as specified in the previous section.
You can use two different authentication methods in the magic8ball chatbot application:
API key: set theAZURE_OPENAI_TYPEenvironment variable toazureand theAZURE_OPENAI_KEYenvironment variable to the key of your Azure OpenAI resource. You can use the regional endpoint, such as https://eastus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/, in theAZURE_OPENAI_BASEenvironment variable, to connect to the Azure OpenAI resource.Azure Active Directory: set theAZURE_OPENAI_TYPEenvironment variable toazure_adand use a service principal or managed identity with the DefaultAzureCredential object to acquire a security token from Azure Active Directory. For more information on the DefaultAzureCredential in Python, see Authenticate Python apps to Azure services by using the Azure SDK for Python. Make sure to assign theCognitive Services Userrole to the service principal or managed identity used to authenticate to your Azure OpenAI Service. For more information, see How to configure Azure OpenAI Service with managed identities. If you want to use Azure AD integrated security, you need to create a custom subdomain for your Azure OpenAI resource and use the specific endpoint containing the custom domain, such as https://myopenai.openai.azure.com/ where myopenai is the custom subdomain. If you specify the regional endpoint, you get an error like the following:Subdomain does not map to a resource. Hence, pass the custom domain endpoint in theAZURE_OPENAI_BASEenvironment variable. In this case, you also need to refresh the security token periodically.
Build the container image
You can build the container image using the Dockerfile and 01-build-docker-image.sh in the scripts folder.
Dockefile
01-build-docker-image.sh
Before running any script, make sure to customize the value of the variables inside the 00-variables.sh file. This file is embedded in all the scripts and contains the following variables:
Upload Docker container image to Azure Container Registry (ACR)
You can push the Docker container image to Azure Container Registry (ACR) using the 03-push-docker-image.sh script in the scripts folder.
03-push-docker-image.sh
Deployment Scripts
If you deployed the Azure infrastructure using the Terraform modules provided with this sample, you only need to deploy the application using the following scripts and YAML templates in the scripts folder.
Scripts
09-deploy-app.sh10-create-ingress.sh11-configure-dns.sh
YAML manifests
configMap.ymldeployment.ymlingress.ymlservice.yml
If you instead want to deploy the application in your AKS cluster, you can use the following scripts to configure your environment.
04-create-nginx-ingress-controller.sh
This script installs the NGINX Ingress Controller using Helm.
05-install-cert-manager.sh
This script installs the cert-manager using Helm.
06-create-cluster-issuer.sh
This script creates a cluster issuer for the NGINX Ingress Controller based on the Let's Encrypt ACME certificate issuer.
07-create-workload-managed-identity.sh
This script creates the managed identity used by the magic8ballchatbot and assigns it the Cognitive Services User role on the Azure OpenAI Service.
08-create-service-account.sh`
This script creates the namespace and service account for the magic8ball chatbot and federate the service account with the user-defined managed identity created in the previous step.
09-deploy-app.sh`
This script creates the Kubernetes config map, deployment, and service used by the magic8ball chatbot.
10-create-ingress.sh
This script creates the ingress object to expose the service via the NGINX Ingress Controller.
11-configure-dns.sh
This script creates an A record in the Azure DNS Zone to expose the application via a given subdomain (e.g., https://magic8ball.example.com).
The scripts used to deploy the YAML template use the yq tool to customize the manifests with the value of the variables defined in the 00-variables.sh file. This tool is a lightweight and portable command-line YAML, JSON and XML processor that uses jq like syntax but works with YAML files as well as json, xml, properties, csv and tsv. It doesn't yet support everything jq does - but it does support the most common operations and functions, and more is being added continuously.
YAML manifests
Below you can read the YAML manifests used to deploy the magic8ball chatbot to AKS.
configmap.yml The configmap.yml defines a value for the environment variables passed to the application container. The configmap does not define any environment variable for the OpenAI key as the container.
These are the parameters defined by the configmap:
AZURE_OPENAI_TYPE: specifyazureif you want to let the application use the API key to authenticate against OpenAI. In this case, make sure to provide the Key in theAZURE_OPENAI_KEYenvironment variable. If you want to authenticate using an Azure AD security token, you need to specifyazure_adas a value. In this case, don't need to provide any value in theAZURE_OPENAI_KEYenvironment variable.AZURE_OPENAI_BASE: the URL of your Azure OpenAI resource. If you use the API key to authenticate against OpenAI, you can specify the regional endpoint of your Azure OpenAI Service (e.g., https://eastus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/). If you instead plan to use Azure AD security tokens for authentication, you need to deploy your Azure OpenAI Service with a subdomain and specify the resource-specific endpoint url (e.g., https://myopenai.openai.azure.com/).AZURE_OPENAI_KEY: the key of your Azure OpenAI resource. If you setAZURE_OPENAI_TYPEtoazure_adyou can leave this parameter empty.AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT: the name of the ChatGPT deployment used by your Azure OpenAI resource, for examplegpt-35-turbo.AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL: the name of the ChatGPT model used by your Azure OpenAI resource, for examplegpt-35-turbo.TITLE: the title of the Streamlit app.TEMPERATURE: the temperature used by the OpenAI API to generate the response.SYSTEM: give the model instructions about how it should behave and any context it should reference when generating a response. Used to describe the assistant's personality.
deployment.yml
The deployment.yml manifest is used create a Kubernetes deployment that defines the application pods to create. azure.workload.identity/use label is required in the pod template spec. Only pods with this label will be mutated by the azure-workload-identity mutating admission webhook to inject the Azure specific environment variables and the projected service account token volume.
service.yml
The application is exposed using a ClusterIP Kubernetes service.
ingress.yml
The ingress.yml manifest defines a Kubernetes ingress object used to expose the service via the NGINX Ingress Controller.
The ingress object defines the following annotations:
- cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: specifies the name of a cert-manager.io ClusterIssuer to acquire the certificate required for this Ingress. It does not matter which namespace your Ingress resides, as ClusterIssuers are non-namespaced resources. In this sample, the cert-manager is instructed to use the
letsencrypt-nginxClusterIssuer that you can create using the06-create-cluster-issuer.shscript. - cert-manager.io/acme-challenge-type: specifies the challend type.
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: specifies the connection timeout in seconds.
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: specifies the send timeout in seconds.
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: specifies the read timeout in seconds.
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-next-upstream-timeout: specifies the next upstream timeout in seconds.
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: allows additional configuration to the NGINX location.
Review deployed resources
Use the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell to list the deployed resources in the resource group.
Azure CLI
PowerShell
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the resources you created, delete the resource group. This will remove all the Azure resources.
Azure CLI
PowerShell
