This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: Healthcare and Life Sciences Blog articles.
How to deploy CM client to Azure AD Joined Cloud PC devices “without Cloud Management Gateway”?
If you’re here it means you’re tracking the main deck for Windows 365 Cloud PC Healthcare Blog Series
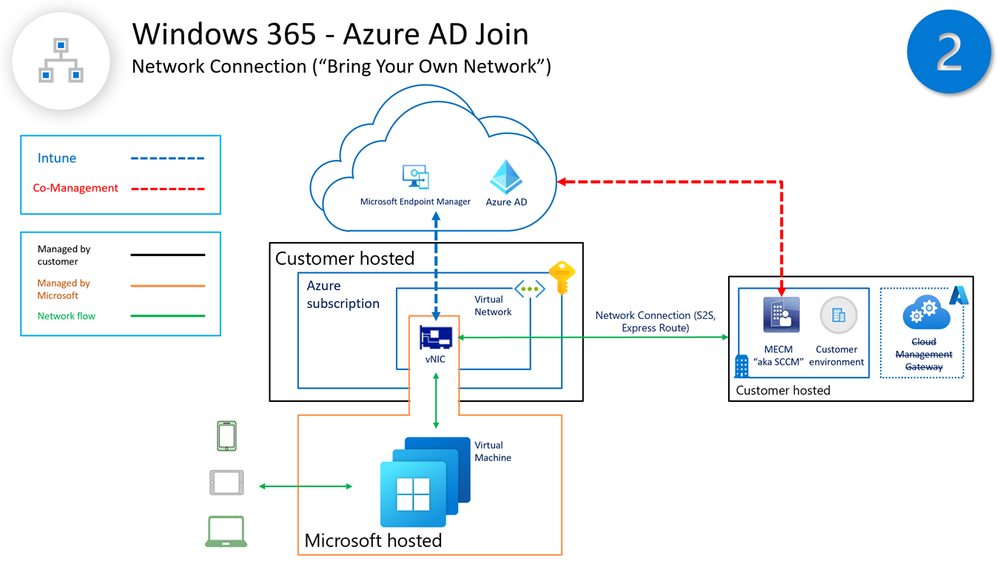
This article is directly associated with Management Design options for Windows 365 Cloud PC (Intune and Co-Management), but solely focused on Windows 365 Cloud PC Architecture Design Provisioning OPTION 2 (Windows 365 Azure AD Joined + hosted in Customer Network).
OPTION 2 teach us about Windows 365 provisioning hosting design option for Cloud PCs and recommendations aligned for management of the device, primarily recommended to leverage Intune through Microsoft Endpoint Manager, your single-pane-of-glass for all your device management needs.
But, what if your MECM (Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Management) server “aka SCCM” PC management solution is well developed and there’s a need to continue to leverage the solution to manage Azure AD Joined Cloud PCs?
Many of our HLS customers leverage Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager as a PC management solution, with wider development on application delivery, device restrictions, PS scripts, reporting, etc... We often receive requests on “how can we manage Azure AD Joined Cloud PCs with MECM servers, do we need a Cloud Management Gateway (CMG)?”
“Azure AD Joined devices are considered internet-based devices because they don’t have a direct connection to an on-premises environment. CMG is leveraged to deliver that PC management needs from MECM servers to manage the Azure AD Joined devices, this gives line-of-sight to MECM on-prem environment” … You can read here for more information.
Tutorial - Enable co-management for internet devices - Configuration Manager | Microsoft Docs
Luckily, OPTION 2 has it benefits!
You could deploy CM clients to Azure AD Joined Cloud PCs managed by MECM servers “without a Cloud Management Gateway (CMG)” by leveraging the existing Windows 365 OPNC connector (On-premises Network Connection) that could be tailored to give line-of-sight to your on-premises MECM environment.
Let’s dive in!
Deploy CM Client for Azure AD Joined Cloud PC (no CMG)
In this business scenario we will deploy the CM client with Intune as a Win32 app to an Azure AD Joined Cloud PC, without a CMG (Cloud Management Gateway)
- CMG is typically required for Azure AD Joined windows devices outside the network to push the CM client from SCCM
- “OPTION 2” (Windows 365 Azure AD Joined + hosted in Customer Network) can leverage the OPNC connector
- OPNC connector can be tailored to give line-of-sight to the on-premises environment (including DCs and SCCM servers)
- With this option we can push the CM client from Intune without CMG
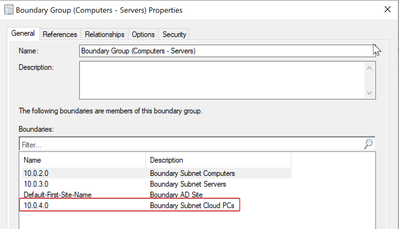
Build the Cloud PC Subnet Boundaries
- First, we need to capture the Cloud PC Subnet address
Azure Portal (https://portal.azure.com) > “Cloud PC” Virtual Network > “Cloud PC” Subnet
- Now we go to MECM server to configure the Cloud PC subnet boundaries
Administration > Boundaries > Add the Cloud PC Subnet (e.g., based on my lab is 10.0.4.0)
Deploy the CM client as an MSI package
1. Intune WIM file
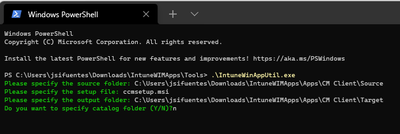
Create a directory where you will package the script as an Intune WIM file
DIRECTORY = "C:\Users\jsifuentes\Downloads\IntuneWIMApps\Apps\CM Client"
Create two folders Source and Target
SOURCE = "C:\Users\jsifuentes\Downloads\IntuneWIMApps\Apps\CM Client\Source"
TARGET = "C:\Users\jsifuentes\Downloads\IntuneWIMApps\Apps\CM Client\Target"
Copy the CM Client MSI application to the Source folder from the SCCM server
PATH "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\bin\i386\ccmsetup.msi"
APPLICATION = "ccmsetup.msi"
Create a folder for the IntuneWinAppUtil tool
TOOLS = "C:\Users\jsifuentes\Downloads\IntuneWIMApps\Tools"
Download IntuneWinAppUtil and copy to the Tools folder
From the folder run Terminal and execute the IntuneWinAppUtil tool
Follow the prompts to copy the SOURCE, APPLICATION and TARGET
The new Intune WIM file will be created
2. Intune Win32 app
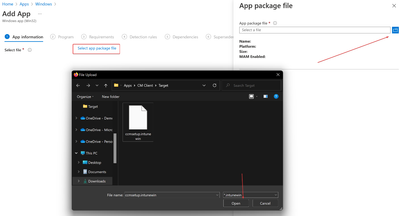
From MEM console https://endpoint.microsoft.com/ > Apps > Windows > Add a Win32 App
Select the WIM file we created
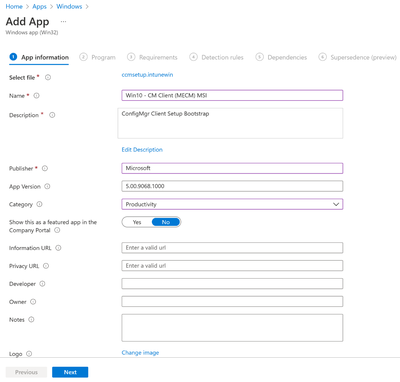
App information named "Win10 - CM Client (MECM)"
Program details
INSTALL command:
UNINSTALL command:
/mp <<<this is the FQDN of your SCCM server>>>
/SMSSITECODE <<<this is the SITE CODE of your SCCM server, it's 3 letters>>>
/SMSMP <<<this is the FQDN of your SCCM server>>>
/DNSSUFFIX <<<this is your local DOMAIN name>>>
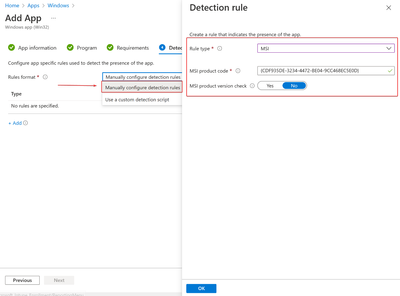
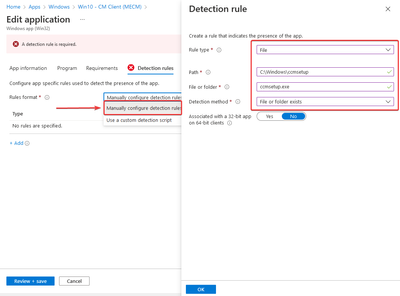
Detection Rules
Option1:
Use the existing MSI rule that gets automatically populated from the MSI client package
MSI product code = {CDF935DE-3234-4472-BE04-9CC468EC5E0D}
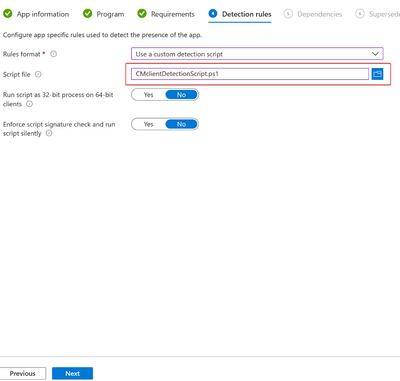
Option2:
Create a detection PS script and save the file as "CMclientDetectionScript.ps1":
Save the PS script to the folder SOURCE
Upload the PS script to Intune Detection rule, keep the defaults
Option3:
Create a detection path to validate if the CM client was previously installed
PATH = C:\Windows\ccmsetup
FILE = ccmsetup.exe
Assign and Create the Win32 app to the Cloud PC device group where the CM client will be installed
Note: you should assign it AFTER the Cloud PC has completed provisioning
Logs
Important logs location under the Cloud PC device to help troubleshoot
C:\Windows\CCMsetup\Logs
C:\Windows\CCM\Logs\ClientLocation.log
C:\Windows\CCM\Logs\LocationServices.log
Discover CM Client manual installs
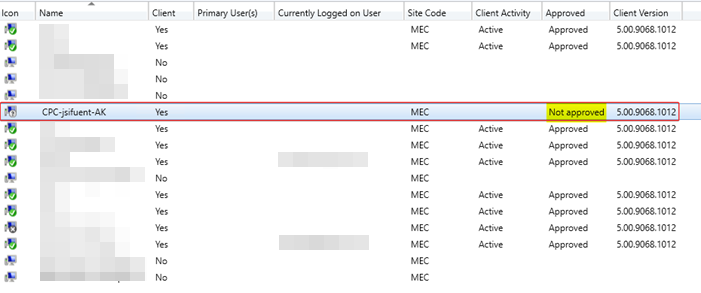
The MECM server won't automatically approve the CM client installation, you'll have to manually approve it (create a collection "Not Approved" to make it easier to find them)
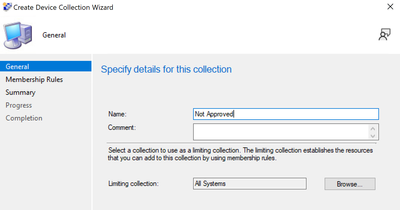
1. Create a Collection “Not Approved”
To help find the Azure AD Joined CPCs after you install the CM client
Assets and Compliance > Device Collections > create collection named "Not Approved" > Limit collection to "All Systems"
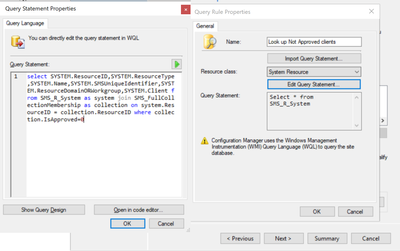
Create query for "Look up Not Approved clients" > Edit query > Show query language:
<<<collection.IsApproved=0 = the value 0 represents all computers where the CM client has not been approved yet>>>
Add columns "Approved" and "Domain" to help identify them
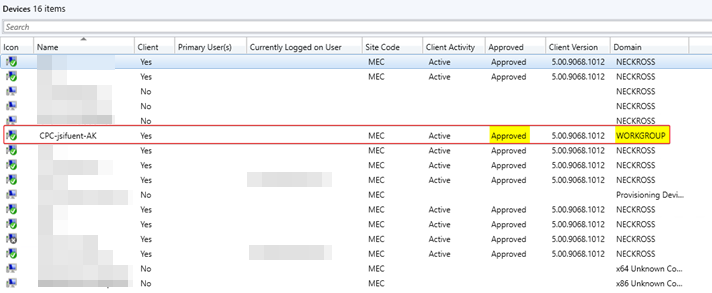
2. Approve the CM client
The CM client will be missing some of the MECM configuration actions until you approve the installation
After Approve, the device will pick up the missing actions from MECM server
From MEM portal, the device will change from (Intune) to (Co-Managed)
Now you will notice the Co-Management workloads are enabled for the Co-Managed Azure AD Joined Cloud PC device
Resources
If you want to learn more about deploying the CM client based on different business scenarios to allow the MECM (Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager) “aka SCCM” server to manage Azure AD Windows devices (Hybrid Domain Joined or Azure Domain Joined), please see the articles below.
Deploy clients to Windows - Configuration Manager | Microsoft Docs
Client installation parameters and properties - Configuration Manager | Microsoft Docs
Bookmark this link for Windows 365 Cloud PC Series: https://aka.ms/HLSWindows365
Thanks for visiting – Juan Sifuentes LinkedIn