This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: New blog articles in Microsoft Tech Community.
Introduction
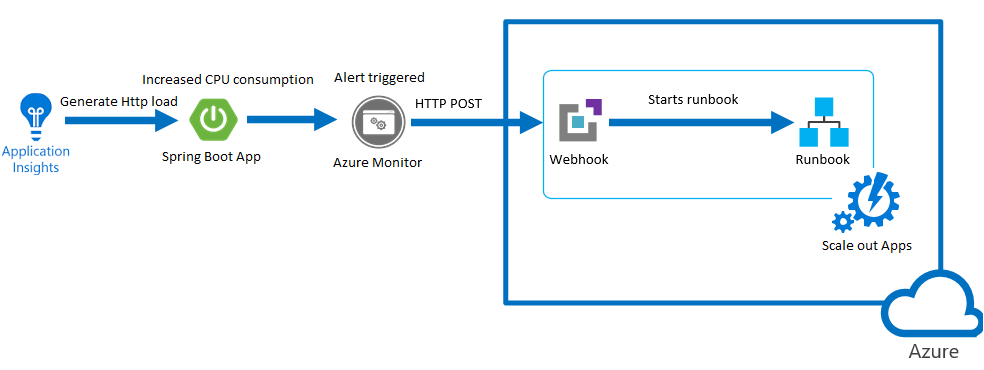
Auto scale is an automation mechanism that scales resources for your apps based on a predefined set of conditions. Auto scale is a critical aspect of application lifecycle management, especially in a cloud computing environment, where you have vast amount of resources at disposal. With the right auto scale strategy, you can optimize your Azure bill and only pay for resources when you really need them. In this blog I will auto scale Azure Spring Cloud with Azure Monitor and Azure Automation Runbooks in 4 steps. The methodology described here is a generic approach and will work with other Azure services as well. We will use the following components to build our automation and let’s cover some concepts first.
- Azure Run As account: Azure automation account provides a container for your Azure Automation resources. When you create a Azure Run As account, it creates a new service principal in Azure Active Directory and assigns the Contributor role to this user at the subscription level. In our case, we will use the service principal created from the Azure Run As account to scale out apps.
- Webhook: Webhook is a http callback endpoint. We will use it when an alert is triggered.
- Alerts from Azure Monitor: Define alert conditions and actions based on resources consumed.
- Performance testing from Application Insights: We will use performance testing from Application Insights to generate http load and trigger alerts.
In the automation flow, we will first generate http load from Application Insights. This will put pressure on our gateway service and increase App CPU consumption. Based on conditions defined, alerts will then be trigger and a webhook callback action is performance. The webhook will invoke an Azure Automation Runbook, which scales out our Spring Boot app.
We’ll use Piggymetrics as our Spring Boot app. You can follow instructions here to create an Azure Spring Cloud instance and deploy Piggymetrics. Now let’s get started on building the automation.
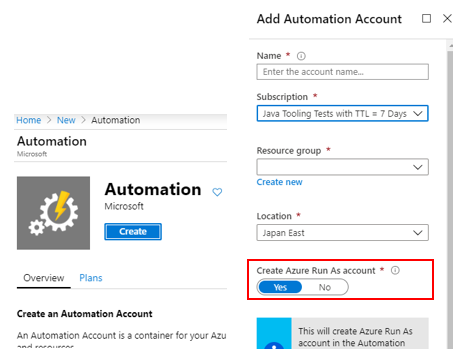
Step 1 – create an automation account
From the Azure marketplace search for “automation”. Pick yes to create an Azure Run As account in the service creation step.
Step 2 – create automation runbook
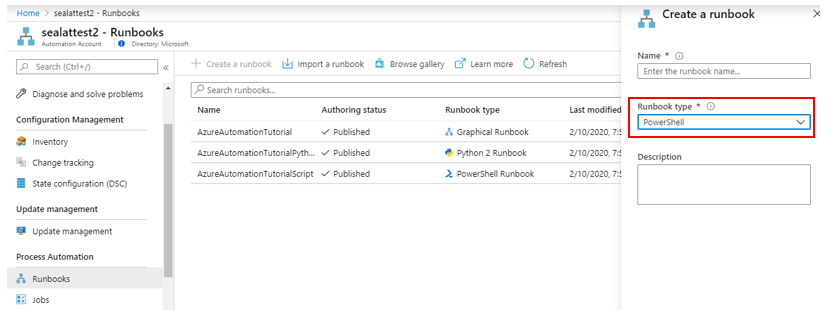
Once the automation account is created, head over to the process automation section of the automation account and click on runbooks. Create a runbook and pick PowerShell as the runbook type.
Copy and paste the code snippet in the PowerShell editor.
param
(
[Parameter (Mandatory = $false)]
[object] $WebhookData
)
#connect to Azure using Azure Run As account
Write-Output "Authenticating to Azure with service principal and certificate"
$ConnectionAssetName = "AzureRunAsConnection"
$servicePrincipalConnection = Get-AutomationConnection -Name $ConnectionAssetName
"Logging in to Azure..."
Connect-AzAccount `
-ServicePrincipal `
-TenantId $servicePrincipalConnection.TenantId `
-ApplicationId $servicePrincipalConnection.ApplicationId `
-CertificateThumbprint $servicePrincipalConnection.CertificateThumbprint
if(-Not $WebhookData.RequestBody)
{
#allow test in test pane
$WebhookData=(ConvertFrom-Json -InputObject $WebhookData)
#convert webhook data to a Json object
$WebhookData=(ConvertFrom-Json -InputObject $WebhookData.RequestBody)
}
else
{
#convert webhook data to a Json object
$WebhookData=(ConvertFrom-Json -InputObject $WebhookData.RequestBody)
}
#retrieve alert data from webhook
$AlertContext=$WebhookData.data.context
#parse the name of the app that triggered the alert
$AppName = $AlertContext.condition.allof.dimensions | where {$_.name -eq "AppName"}
#appname is case sensitive as a part of the Azure resource ID. All my app names are lower case. In some cases Alert will
#capitalize the first letter of appname in the alert context. Make sure the case type matches with the name of your app.
$AppName = $AppName.value.ToLower()
$resourceId = ( $AlertContext.resourceId + '/apps/' + $AppName + '/deployments/default')
#scale the app out by adding 1 more app instance
$Resource = Get-AzResource -ResourceId $resourceId
#retrieve current instance count and convert it to a number
$IC = $Resource.Properties.deploymentSettings.instanceCount
[int]$CurrentInstanceCount = [convert]::ToInt32($IC, 10)
$TargetInstanceCount = $CurrentInstanceCount + 1
Write-Output ( 'Scaling ' + $AppName.value + ' instance count from ' + $CurrentInstanceCount +' to ' + $TargetInstanceCount)
$Resource.Properties.deploymentSettings.instanceCount=$TargetInstanceCount
$Resource | Set-AzResource -Force
Write-Output 'Scaling completed'
Save and publish the runbook.
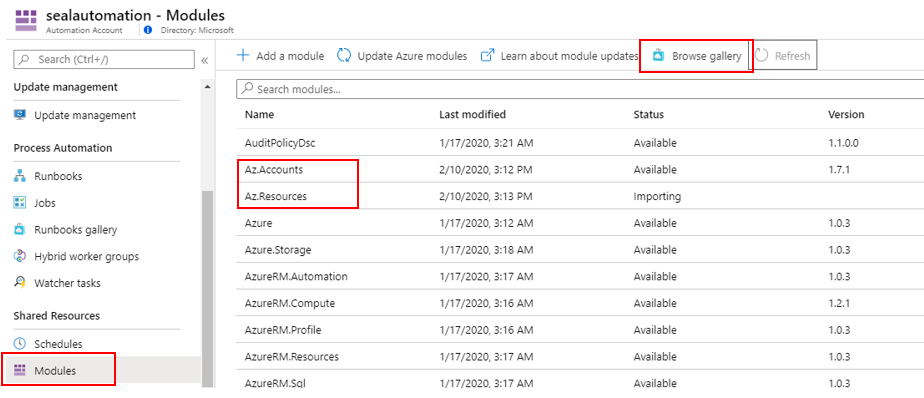
Lastly, we need to import dependencies for the PowerShell modules used in the code snippet. Go back to the automation account, under modules, click on browse gallery and import Az.Accounts and Az.Resources.
Step 3 – Add a webhook
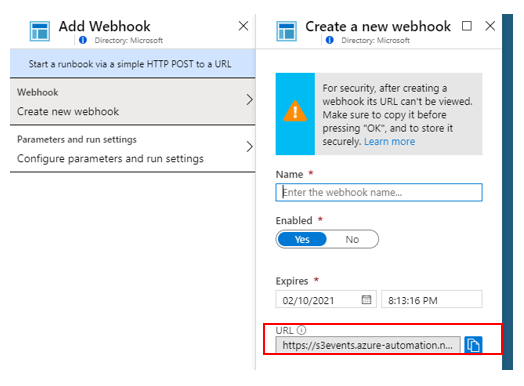
From the overview menu of the runbook, click on Add webhook. An URL which includes a security token will be auto generated. Make sure you copy this URL and save it somewhere safe as it will not be available to you once the webhook is created.
Leave everything else as default in the parameters and run settings menu. Click on create to create the webhook.
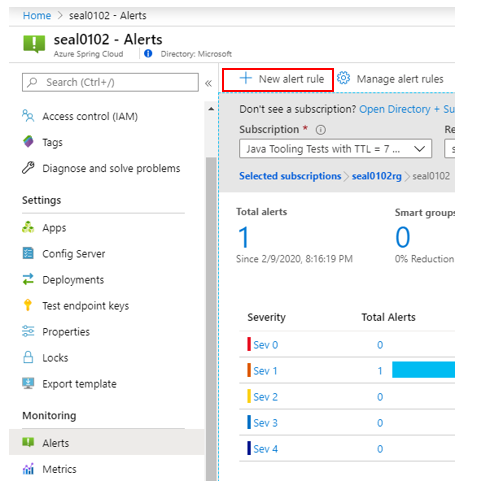
Step 4 – Add an alert and connect it with the webhook
Add a new alert rule from Alerts under the Monitoring section of your Azure Spring Cloud service instance.
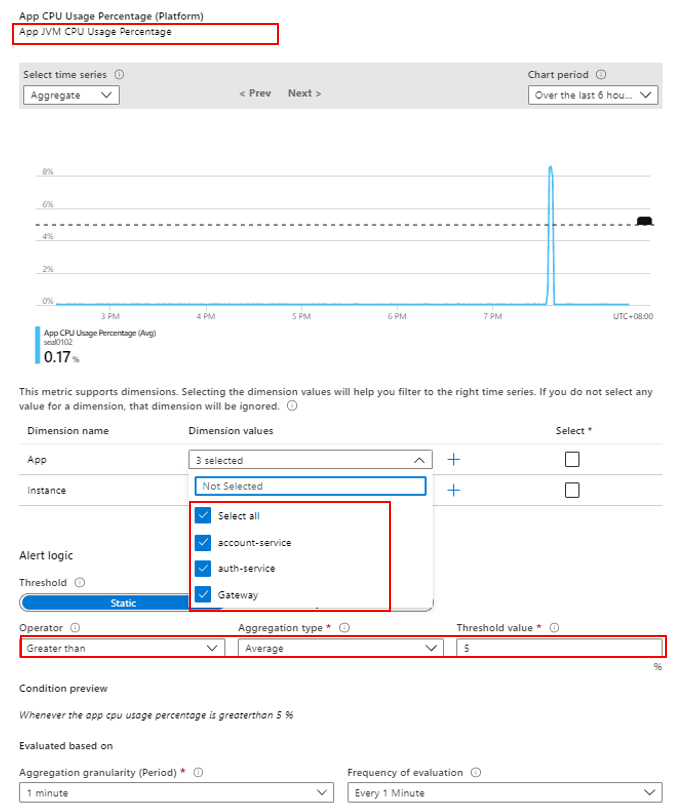
- Select “App CPU Usage Percentage (Platform)” under signal type.
- Select all services in the app dimension
- Set the alert to go off when average consumption is greater than 5%
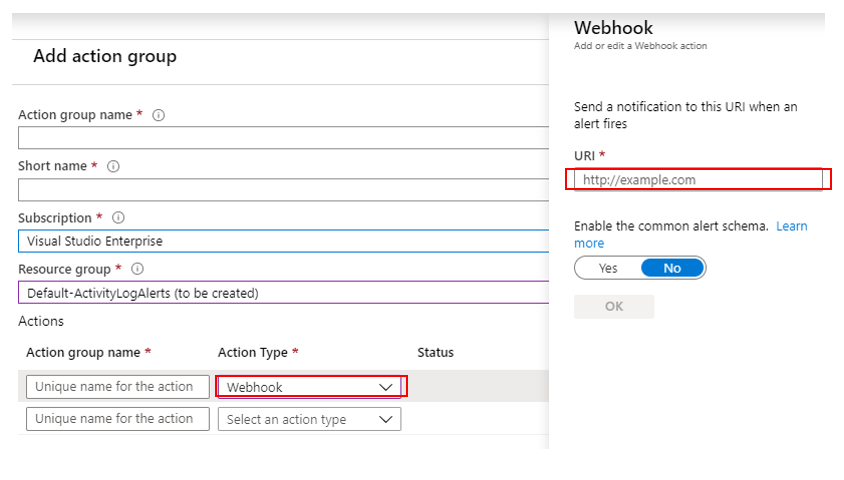
Create a new action group for the alert condition. Pick webhook in the action type and paste the webhook callback URI that you save in step 3.
Step 4 – Test auto scale
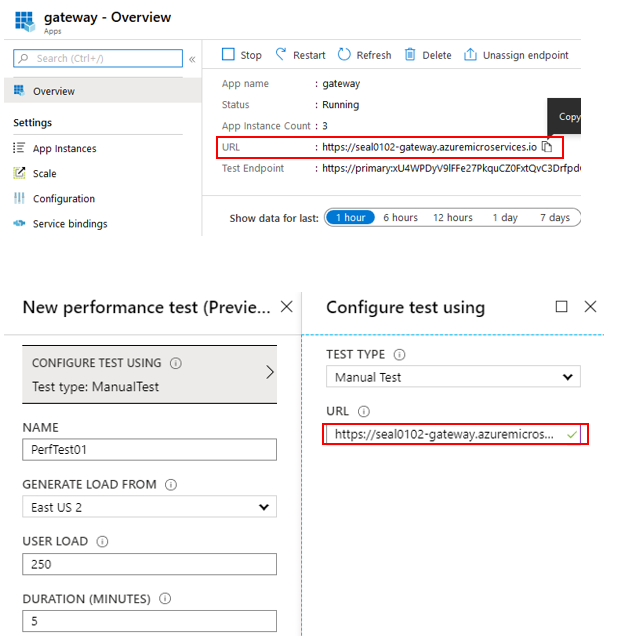
To trigger the auto scale we will need to generate some load to get the average CPU consumption above 5%. I will use Azure Application Insights for this task. Create an Application Insights instance from the Azure portal and click on performance testing under the configure menu. Click on new and choose manual test under test type. Copy and paste the public endpoint of the piggymetrics gateway app and Click on run test.
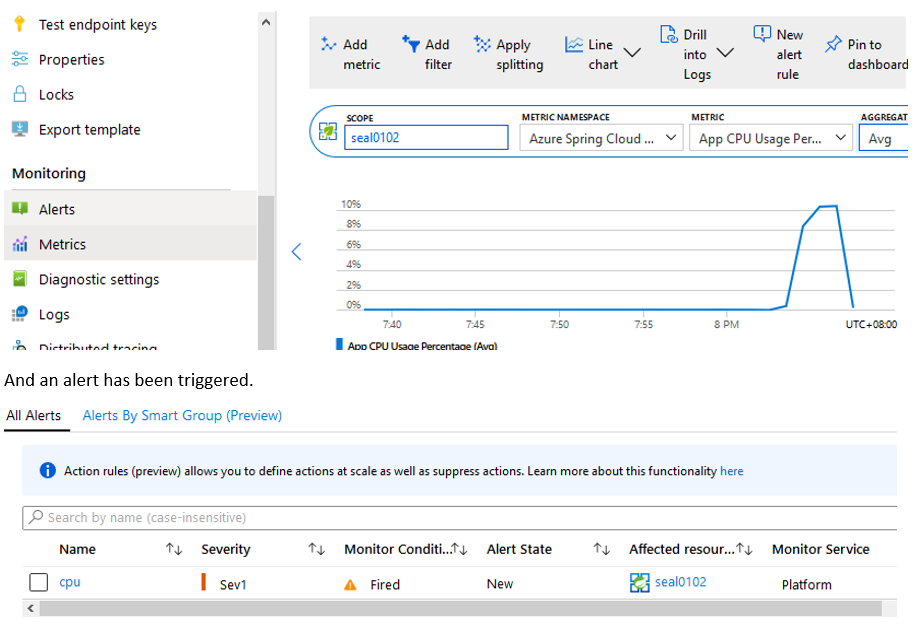
After the load test is complete, let’s head back to Metrics under the Monitoring section of our Azure Spring Cloud instance. We see our average App CPU usage crept up to 10% during the load test.
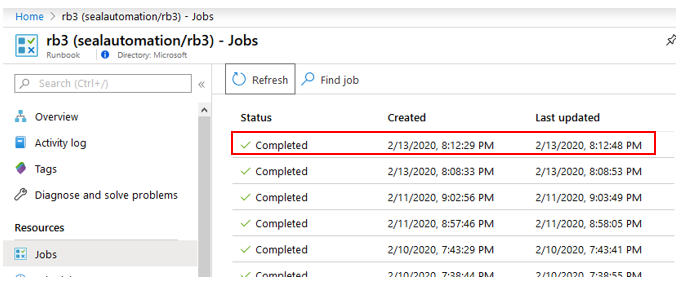
Next we will check recent jobs under our automation account, and we see a new job has completed. Click on the job entry in the table to see details of this job.
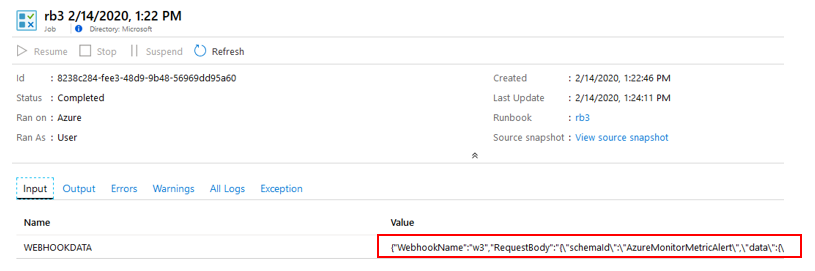
You can find the input of the webhook data from the input tab. You can copy this data and use it as the input parameter when customizing the auto scale script.
The output tab shows output from the automation script, and you will see “Set-AzResource : The operation failed because resource could not be de-serialized.” Under the errors tab. You can ignore this message.
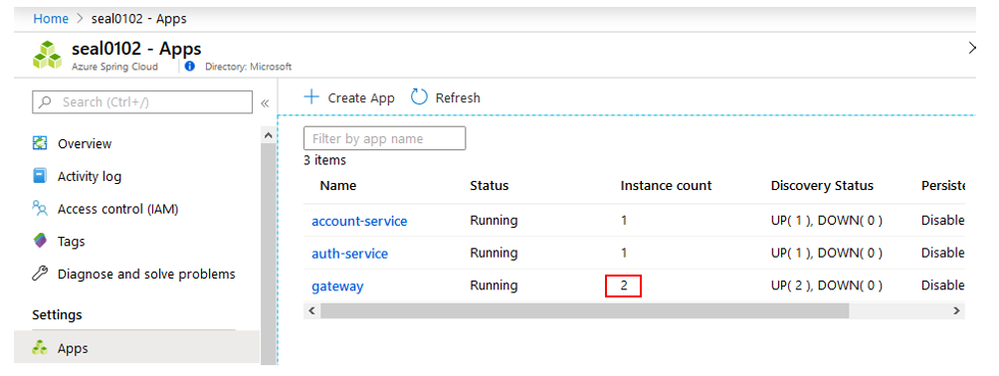
Finally, go back to your Azure Spring Cloud instance and verify that the gateway service has been scaled out to 2 instances.
Closing remarks
Congratulations, you’ve now set up auto scaling for you Azure Spring Cloud apps. Consider the following steps to take this setup for production.
- Test and customize the automation script against your webhook, as your webhook input data may be different.
- Figure out the right auto scale strategy based on your usage patterns, and the types of resources consumed by your apps.
- Follow best practices for auto scale.
- For advance load test scenarios you can use Gatling. It requires programing in Scala, but you can record test actions and replay them in scripts, once you configure Gatling as your local proxy in the browser.