This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: Azure Developer Community Blog articles.
How to containerize and deploy a Java app to Azure
Use containers for platform independence
An application that runs in a container behaves the same, wherever you run it. That's because the container provides a stable infrastructure environment that doesn't change. You just take it to wherever you want to run it.
This also enables you to run self-contained applications that do not rely on a runtime, like the Java runtime, to be installed on its host. And this experience is enhanced with cloud-based management and features when you run your containers in a service like Azure Kubernetes Service.
In this post, we'll containerize a Java application, push it to Azure Container Registry, and run it in Azure Kubernetes Service.
Prerequisites
If you want to follow along, you'll need the following:
* An Azure subscription (If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin)
* The latest version of Visual Studio Code
* The Git CLI
* And the latest version of the Azure CLI
Containerize a Java app and deploy it to Azure Kubernetes Service
In this post, we'll focus on the containerization and deployment of a Java application. Because of that, we start with an existing Azure Kubernetes Service and an Azure Container Registry. Let's get started.
1. Open Visual Studio Code
2. Go to View > Command Palette and type Git: Clone and select the first result
3. Enter the following URL, which is for a sample Java application:
4. Hit Enter and select a location to clone the Git repo
5. When asked, click "Open" to open the Java application

(Sample Java application in VS Code)
6. We need to add a Dockerfile to the code to be able to containerize it. Navigate to Project > Airlines in the source code and add a new file with the name "Dockerfile", without a file extension
7. When VS Code detects that you added a Dockerfile, it will prompt you to install the Docker extension. Click Install to install the extension
8. Go back to the newly created Dockerfile and paste in the following code. This specifies a build and package process to containerize the application:
9. Next, we'll build the container. Open a terminal window by right-clicking on the Airlines folder in the file explorer of VS Code, and selecting "Open in integrated terminal"
10. In the terminal, execute the following command to build the container:
11. When the build is complete, test the application locally by running the command below:
12. You'll be able to use the application when you open http://localhost:8080/FlightBookingSystemSample in a local browser
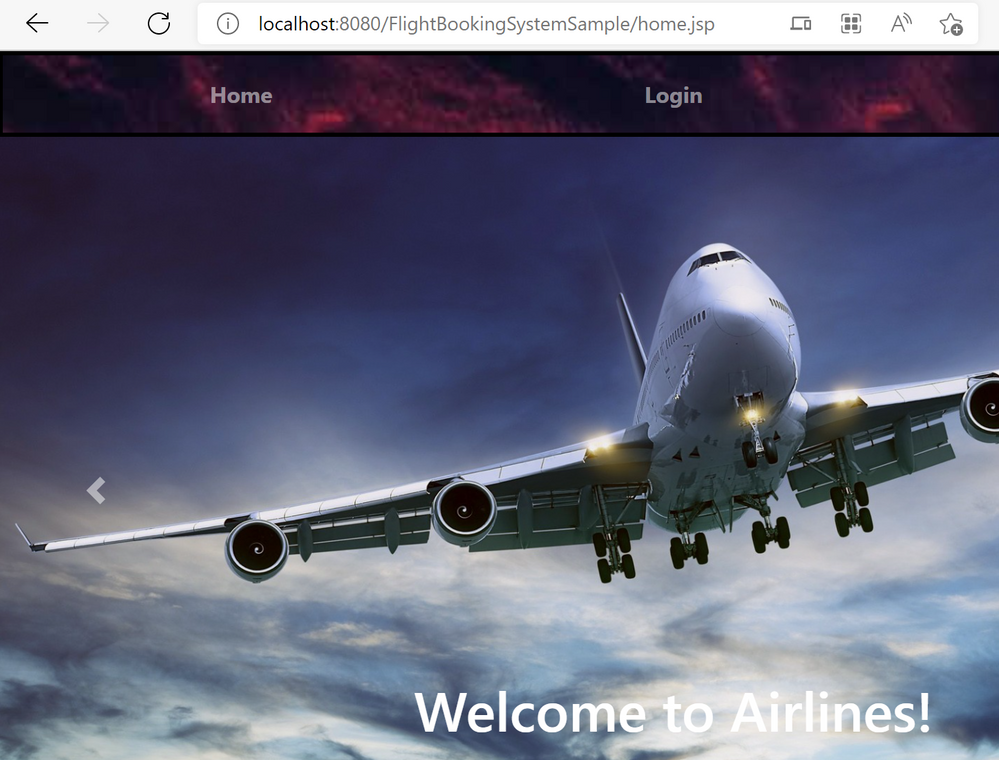
(The containerized Java application running locally)
13. Now that we've successfully containerized the application, we will push it to Azure Container Registry and run it in Azure Kubernetes Service. Make sure that you have the names of the resource group that these services are deployed in, and that you have the names of the Azure Container Registry and Azure Kubernetes Service
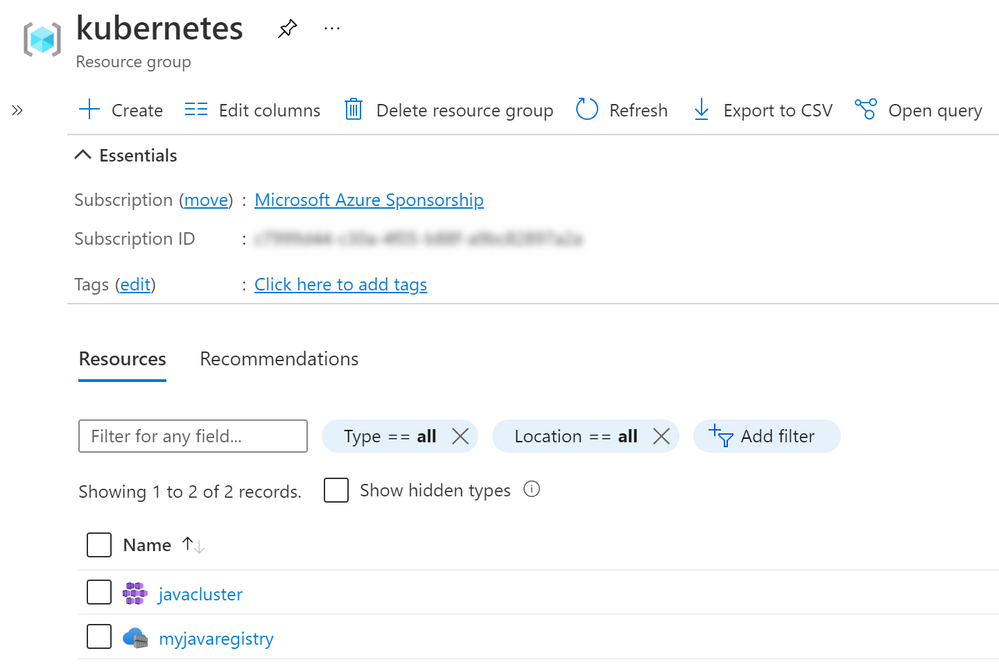
(The resource group and service names in Azure)
14. We'll feed the resource group and service names into parameters that we can use in later scripts by executing the following command: (replace the values with your own)
15. First, make sure that you are logged into Azure by running:
16. Next, log into the Azure Container Registry:
17. Now tag the previously built container image with your Azure Container Registry:
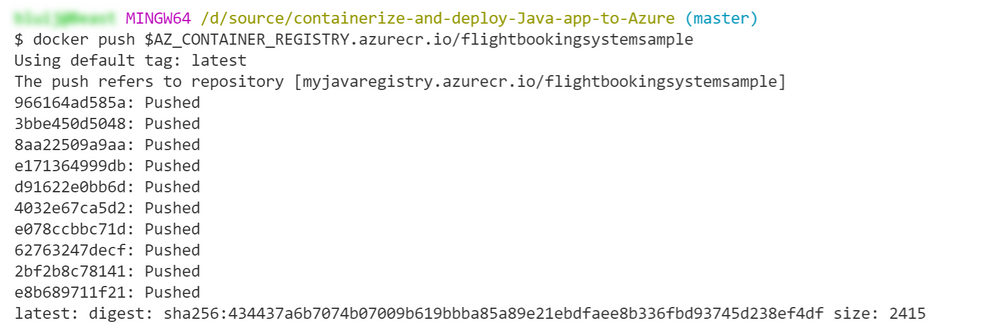
18. Push the container to Azure Container Registry:
(Push the container to Azure Container Registry)
19. To deploy the container to Azure Kubernetes Service, we'll add a new file to the source code. In the Project > Airlines folder, add a file with the name "deployment.yml"
20. Paste the following code into the file. Replace the name of the Azure Container Registry with your own. These are instructions to take the container from Azure Container Registry and deploy it into Azure Kubernetes Service:
21. To enable the Azure CLI to deploy the container, we need to install the CLI AKS extension with this command:
22. Next, connect to your Kubernetes cluster:
23. Now apply the deployment file to start the deployment:
24. Check the deployment with the command below. When it is finished, you'll see that your pod has the status "Running". You can now use the external-ip from service/flightbookingsystemsample to use the application:
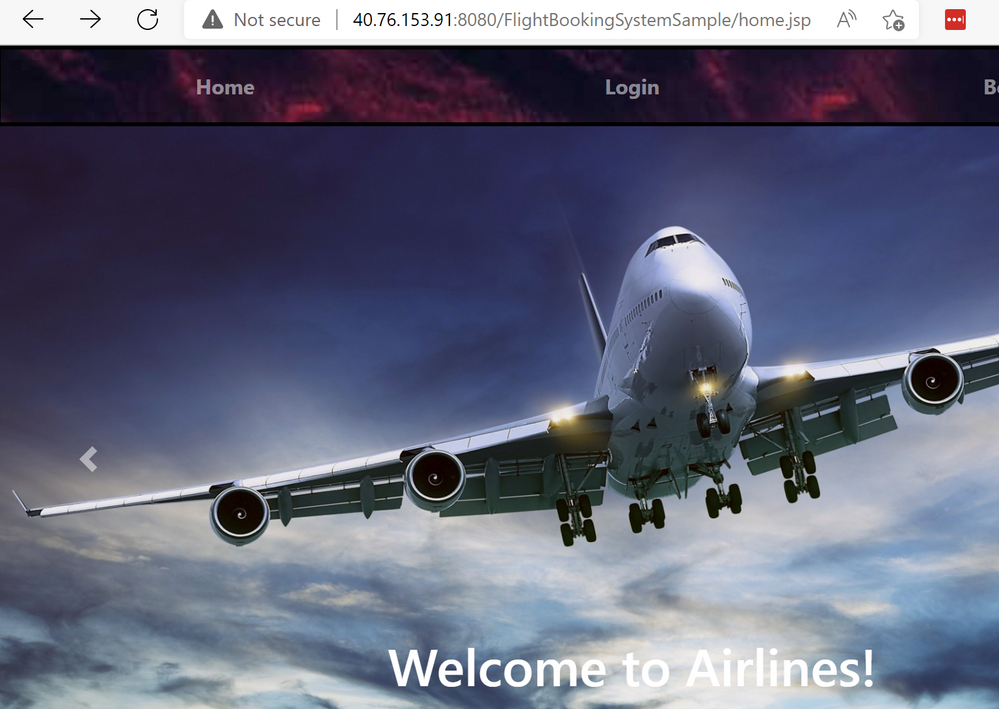
(The containerized Java application running in Azure Kubernetes Service)
Conclusion
Containers provide a programming-language agnostic platform in which to run applications. And with Azure Container Registry and Azure Kubernetes Service, managing and running your containerized applications is easier and more performant. To learn more, create a trial account today and go and check it out!