This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: Microsoft Tech Community - Latest Blogs - .
By Laura Arrizza, Product Manager and Amit Ghodke, Principal Product Manager Architect | Microsoft Intune
In May 2022, Security Settings Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint became generally available. This empowers security teams to configure devices with their desired Antivirus, Endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Firewall settings directly from the Microsoft Intune admin center, without the need for a full device enrollment.
We are expanding our coverage to include settings within the Attack surface reduction (ASR) rules security template with these capabilities.
Evaluating existing profiles
As we move into public preview, you’ll notice the Attack surface reduction rules settings will apply to all devices in the targeted group. This means, if the targeted group contains devices enrolled to Intune via mobile device management (MDM) and devices onboarded via Security settings management, Defender for Endpoint managed devices will start to receive the attack surface reduction rules settings, based on the policy configuration.
Prior to Intune’s 2301 service release, devices in the targeted group that are managed with Defender for Endpoint would’ve shown as ”Not Applicable” for these policy types and wouldn’t have received the policies.
How to determine the impact on existing profiles
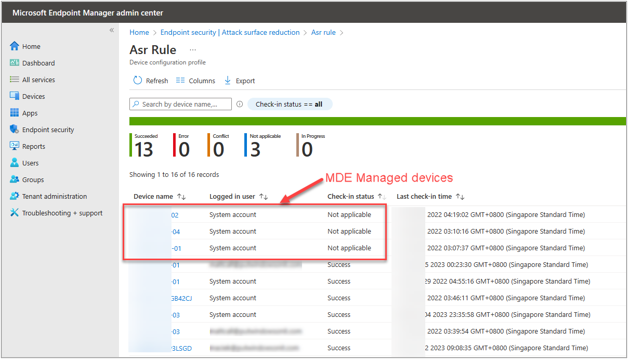
To evaluate the impacted devices, please review any devices with the “Not applicable” status against the attack surface reduction rules settings in Intune. If you have devices that show as “Not applicable” and those devices also show as “Managed by MDE,” the public preview will result in them starting to process the policies.
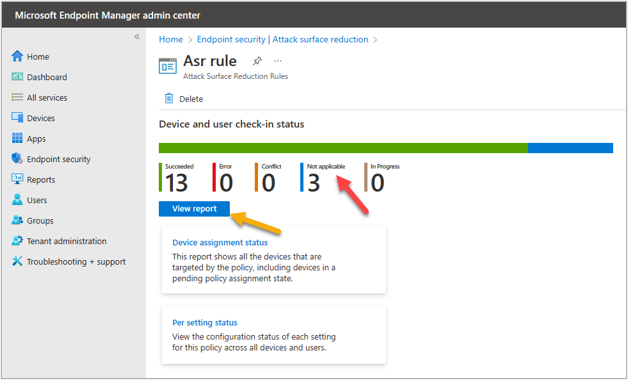
Below are examples of per policy report against the configured policy and Windows devices as seen under the “Devices” blade in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
Under the Endpoint security blade, select the appropriate policy and click on it to view the policy report.

If you would like to exclude these devices from the policy, follow the steps in the following section to create an exclusion group for Defender for Endpoint managed devices and adjust the policy targeting with this exclusion group.
Excluding MDE devices from scope
Depending on the intent of your organization, you may want to exclude devices from receiving the attack surface reduction rules settings. To do this, create groups of Defender for Endpoint managed devices and modify the policy targeting to exclude these devices.
Creating a group to exclude Defender for Endpoint managed devices.
- Using SystemLabel and dynamic group
Device groups can be created and automatically populated using Dynamic Groups in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for targeting.
Step 1: Create a Group in Azure AD as described in: Add groups to organize users and devices.
Step 2: Select Dynamic Device as the Membership type.A screenshot of the options for creating a new group in Intune with the Dynamic Device Membership type option highlighted.
Step 3: Use the MDEManaged label for devices that are using security management for Defender for Endpoint:
• MDEManaged is added to devices that are actively using the security management scenario. This tag is removed from the device if Defender for Endpoint stops managing the security configuration.
Under the Dynamic membership rules, use systemlabels and create a query such as,
(device.systemLabels -contains “MDEManaged“). This will auto-populate the group with the desired set of devices.A screenshot of the Dynamic membership rules pane with the example query added to the Rule syntax in the Configuration Rules settings.
- Device groups can also be created manually using ”Assigned” as the membership type at the time of group creation in Azure AD, which may be used for targeting policies.
Additional considerations
- Assignment filters are currently not supported for devices managed with the Security Management for the Defender for Endpoint scenario. If you’re using filters on your Endpoint security profiles, they’re  for devices managed by Defender for Endpoint.
- For best practices with Intune grouping and targeting, see: Intune grouping, targeting, and filtering: recommendations for best performance.
Keep us posted on your favorite new feature and as always let us know if you have any additional questions or feedback. You can comment on this post or reach out to us on Twitter by tagging us at @IntuneSuppTeam.
