This post has been republished via RSS; it originally appeared at: Azure Data Explorer articles.
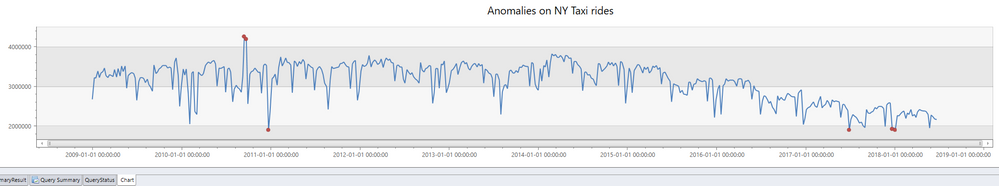
There are many interesting use cases for leveraging machine learning algorithms and derive interesting insights out of telemetry data. Azure Data Explorer, Anomaly Chart creates a time series data that utilizes anomaly detection function series_decompose_anomalies. The anomalies detected by the Kusto service, and are highlighted as red dots on the time series chart.
Anomalychart is a line chart highlights anomalies using series_decompose_anomalies function.
Trips | where pickup_datetime between(datetime(2009-01-01) .. datetime(2018-07-01)) | make-series RideCount=count() on pickup_datetime from datetime(2009-01-01) to datetime(2018-07-01) step 7d | render anomalychart
//Let's use the built-in capabilities to detect anomalies Trips | where pickup_datetime between(datetime(2009-01-01) .. datetime(2018-07-01)) | make-series RideCount=count() on pickup_datetime from datetime(2009-01-01) to datetime(2018-07-01) step 7d | extend anomalies = series_decompose_anomalies(RideCount, 1) | render anomalychart with(anomalycolumns=anomalies,title='Anomalies on NY Taxi rides')
Running the long version let you control the parameters
| render anomalychart use the defaults, specifically the default anomaly threshold is 1.5
so it would be similar to
| extend anomalies = series_decompose_anomalies(num, 1.5)
| render anomalychart with(anomalycolumns=anomalies, title='Web app. traffic of 5 days, Point Anomalies by Time Series Decmposition, Anomaly threshold = 2.0')
read more on Machine Learning and Time Series Analysis
“Join the conversation on the Azure Data Explorer community”.